Configuring EDB Postgres Advanced Server v17
You can easily update parameters that determine the behavior of EDB Postgres Advanced Server and supporting components by modifying the following configuration files:
- The
postgresql.conffile determines the initial values of EDB Postgres Advanced Server configuration parameters. - The
pg_hba.conffile specifies your preferences for network authentication and authorization. - The
pg_ident.conffile maps operating system identities (user names) to EDB Postgres Advanced Server identities (roles) when usingident-based authentication.
For more information about modifying the postgresql.conf and pg_hba.conf files, see Setting parameters.
You can use your editor of choice to open a configuration file. On Windows, you can navigate through the EDB Postgres menu to open a file.
Setting EDB Postgres Advanced Server environment variables
The graphical installer provides a script that simplifies the task of setting environment variables for Windows users. The script sets the environment variables for your current shell session. When your shell session ends, the environment variables are destroyed. You might want to invoke pgplus_env.bat from your system-wide shell startup script, which definies environment variables for each shell session.
The pgplus_env script is created during the EDB Postgres Advanced Server installation process and reflects the choices made during installation. To invoke the script, at the command line, enter:
C:\Program Files\edb\as16\pgplus_env.bat
As the pgplus_env.bat script executes, it sets the following environment variables:
PATH="C:\Program Files\edb\as16\bin";%PATH% EDBHOME=C:\Program Files\edb\as16 PGDATA=C:\Program Files\edb\as16\data PGDATABASE=edb REM @SET PGUSER=enterprisedb PGPORT=5444 PGLOCALEDIR=C:\Program Files\edb\as16\share\locale
If you used an installer created by EDB to install PostgreSQL, the pg_env script performs the same function:
C:\Progra~1\PostgreSQL\16\pg_env.bat
As the pg_env.bat script executes on PostgreSQL, it sets the following environment variables:
PATH="C:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\16\bin";%PATH% PGDATA=C:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\16\data PGDATABASE=postgres PGUSER=postgres PGPORT=5432 PGLOCALEDIR=C:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\16\share\locale
Connecting to EDB Postgres Advanced Server with edb-psql
edb-psql is a command-line client application that allows you to execute SQL commands and view the results. To open the edb-psql client, make sure the client is in your search path. The executable resides in the bin directory under your EDB Postgres Advanced Server installation.
Use the following command and options to start the edb-psql client:
psql -d edb -U enterprisedb
Where:
-d specifies the database to which edb-psql connects.
-U specifies the identity of the database user to use for the session.
If you performed an installation with the interactive installer, you can access the edb-psql client by selecting EDB Postgres > EDB-PSQL. When the client opens, provide connection information for your session.
The edb-psql file is a symbolic link to a binary called psql, a modified version of the PostgreSQL community psql, with added support for EDB Postgres Advanced Server features. For more information about using the command-line client, see the PostgreSQL core documentation.
Connecting to EDB Postgres Advanced Server with the pgAdmin 4 client
pgAdmin 4 provides a graphical interface that you can use to manage your database and database objects. Dialog boxes and online help simplify tasks such as object creation, role management, and granting or revoking privileges. The tabbed browser panel provides quick access to information about the object currently selected in the pgAdmin tree control.
The client is distributed with the graphical installer. To open pgAdmin, select EDB Postgres > pgAdmin4`. The client opens in your default browser.
To connect to the EDB Postgres Advanced Server database server, expand the Servers node of the Browser tree control, and right-click on the EDB Postgres Advanced Server node. From the context menu, select Connect Server. The Connect to Server dialog box opens.
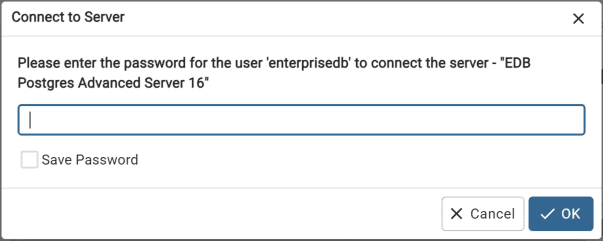
To connect, in the Password field, provide the password associated with the database superuser, and select OK.
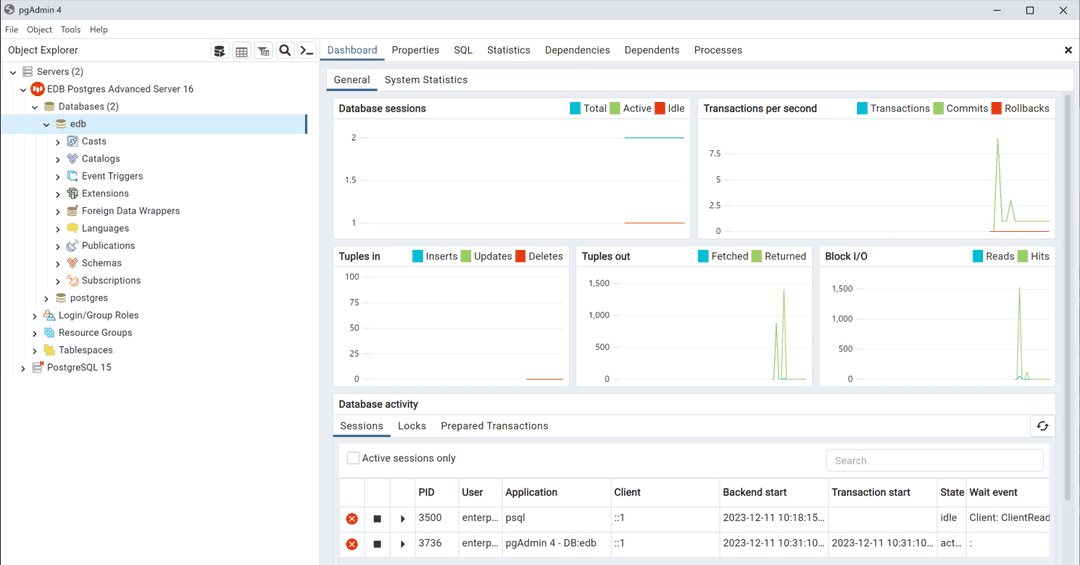
When the client connects, you can use the Browser tree control to retrieve information about existing database objects or to create new objects. For more information about using the pgAdmin client, use the Help menu.