ECPGPlus overview v17
EDB enhanced ECPG (the PostgreSQL precompiler) to create ECPGPlus. ECPGPlus is a Pro*C-compatible version of the PostgreSQL C precompiler. ECPGPlus translates a program that combines C code and embedded SQL statements into an equivalent C program. As it performs the translation, ECPGPlus verifies that the syntax of each SQL construct is correct.
About ECPGPlus
The following diagram charts the path of a program containing embedded SQL statements as it's compiled into an executable:
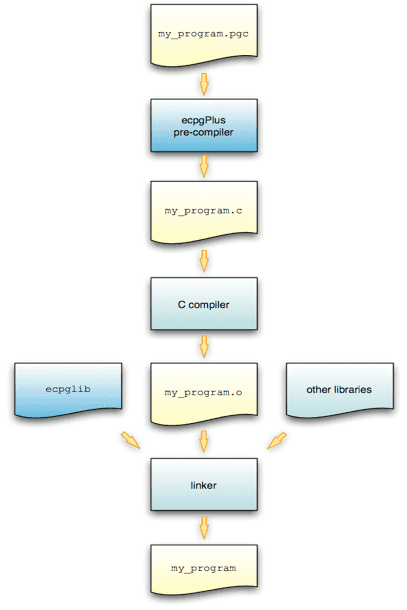
Compilation of a program containing embedded SQL statements
To produce an executable from a C program that contains embedded SQL statements:
- Pass the program (
my_program.pgcin the diagram) to the ECPGPlus precompiler. ECPGPlus translates each SQL statement inmy_program.pgcinto C code that calls theecpglibAPI and produces a C program (my_program.c). - Pass the C program to a C compiler. The C compiler generates an object file (
my_program.o). - Pass the object file (
my_program.o) as well as theecpgliblibrary file and any other required libraries to the linker, which in turn produces the executable (my_program).
While the ECPGPlus preprocessor validates the syntax of each SQL statement, it can't validate the semantics. For example, the preprocessor confirms that an INSERT statement is syntactically correct, but it can't confirm that the table mentioned in the INSERT statement exists.
Behind the scenes
A client application contains a mix of C code and SQL code made up of the following elements:
- C preprocessor directives
- C declarations (variables, types, functions, ...)
- C definitions (variables, types, functions, ...)
- SQL preprocessor directives
- SQL statements
For example:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 EXEC SQL INCLUDE sqlca; 3 4 extern void printInt(char *label, int val); 5 extern void printStr(char *label, char *val); 6 extern void printFloat(char *label, float val); 7 8 void displayCustomer(int custNumber) 9 { 10 EXEC SQL BEGIN DECLARE SECTION; 11 VARCHAR custName[50]; 12 float custBalance; 13 int custID = custNumber; 14 EXEC SQL END DECLARE SECTION; 15 16 EXEC SQL SELECT name, balance 17 INTO :custName, :custBalance 18 FROM customer 19 WHERE id = :custID; 20 21 printInt("ID", custID); 22 printStr("Name", custName); 23 printFloat("Balance", custBalance); 24 }
In this code fragment:
Line 1 specifies a directive to the C preprocessor.
C preprocessor directives can be interpreted or ignored. The option is controlled by a command line option (
-C PROC) entered when you invoke ECPGPlus. In either case, ECPGPlus copies each C preprocessor directive to the output file (4) without change. Any C preprocessor directive found in the source file appears in the output file.Line 2 specifies a directive to the SQL preprocessor.
SQL preprocessor directives are interpreted by the ECPGPlus preprocessor and aren't copied to the output file.
Lines 4 through 6 contain C declarations.
C declarations are copied to the output file without change, except that each
VARCHARdeclaration is translated into an equivalentstructdeclaration.Lines 10 through 14 contain an embedded-SQL declaration section.
C variables that you refer to in SQL code are known as host variables. If you invoke the ECPGPlus preprocessor in Pro*C mode (
-C PROC), you can refer to any C variable in a SQL statement. Otherwise you must declare each host variable in aBEGIN/END DECLARATION SECTIONpair.Lines 16 through 19 contain a SQL statement.
SQL statements are translated into calls to the ECPGPlus runtime library.
Lines 21 through 23 contain C code.
C code is copied to the output file without change.
Prefix any SQL statement with EXEC SQL. The SQL statement extends to the next (unquoted) semicolon. For example:
printf(“Updating employee salaries\n”); EXEC SQL UPDATE emp SET sal = sal * 1.25; EXEC SQL COMMIT; printf(“Employee salaries updated\n”);
When the preprocessor encounters this code fragment, it passes the C code (the first line and the last line) to the output file without translation and converts each EXEC SQL statement into a call to an ecpglib function. The result is similar to the following:
printf("Updating employee salaries\n"); { ECPGdo( __LINE__, 0, 1, NULL, 0, ECPGst_normal, "update emp set sal = sal * 1.25", ECPGt_EOIT, ECPGt_EORT); } { ECPGtrans(__LINE__, NULL, "commit"); } printf(“Employee salaries updated\n”);
- On this page
- About ECPGPlus
- Behind the scenes